Nitrogen and Phosphorus Waste Water Treatment by Denitrification-Hydrolytic Acidification-Anaerobic-Anoxic-MBR Process
An industrial park has a number of LED
manufacturers, manufacturers and machinery manufacturers, and is a
semiconductor production and research and development base. According to the
production process of each plant, the sewage is collected and treated in
stages. The chemical reaction-coagulation sedimentation method is used for the
high-phosphorus wastewater, and the treated wastewater is mixed with the
non-phosphorus wastewater that has been pretreated by various factories, and
then the mixed wastewater is treated by the
denitrification-hydrolysis-acidification-anaerobic-anoxic-MBR process. deal
with.
1 Project overview
1.1 Design water quantity and water quality
The amount of wastewater in the high phosphorus section is
less, and the volume flow is 200 m3/d. The water quality of wastewater is: pH
7-10, COD=186 mg/L, ρ(TP)=16 mg/L, ρ(SS)=120 mg/L.
The wastewater in the high phosphorus section is mixed with
non-phosphating water after treatment, the total volume flow is 1 200 m3/d, and
the designed treatment capacity is 50 m3/h. Mixed influent pH is 6~9, COD=450
mg/L, BOD5=80 mg/L, ρ(TN)=86mg/L, ρ(NO3--N)=50-60 mg/L, ρ(TP )=7.4 mg/L.
1.2 Process flow
The wastewater in the high phosphorus section has the characteristics of high suspended solids and phosphorus content. For such wastewater, the coagulation and sedimentation method is used to remove it.
The pretreated non-phosphate wastewater after treatment by various enterprises has high nitrogen and phosphorus content and low carbon content and the characteristics of low biodegradability, first denitrification treatment of sewage to remove part of nitrate nitrogen, carbon source should be added before denitrification to ensure sufficient carbon source.
The effluent after
denitrification is hydrolyzed and acidified to degrade the refractory
substances in the sewage. Finally, the sewage goes through the A2O process to
remove COD, TN, and TP.
1.3 Design description of main structures
1.3.1 Phosphating wastewater pretreatment conditioning tank
The untreated high phosphorus-containing wastewater from each
enterprise is transported to the sewage treatment plant through tank trucks,
and enters the pretreatment adjustment tank to uniformize the water quality and
quantity of the phosphorus-containing wastewater, and control the sewage to
enter the subsequent treatment facilities according to a certain flow.
1.3.2 Phosphating wastewater coagulation sedimentation tank
After the pH adjustment of the phosphating wastewater, NaOH, calcium chloride, polyaluminum chloride (PAC) and polyacrylamide (PAM) were sequentially added to the wastewater to form large particle precipitation by flocculation.
The inclined plate placed in the precipitation area divides the
precipitation area into several areas, thereby increasing the precipitation
area, accelerating the precipitation speed, improving the precipitation efficiency,
and achieving the purpose of separation of mud and water.
1.3.3 Neutralization treatment reaction tank
Adjust the pH of the effluent from the inclined plate
sedimentation tank to neutral and then discharge it to the non-phosphating
wastewater adjustment tank for further treatment.
1.3.4 Non-phosphating wastewater conditioning tank
The water quality of each enterprise and the treated
phosphating wastewater are uniformly treated to ensure the stability of the
water inflow to the subsequent facilities.
1.3.5 Primary sedimentation tank
The pool is provided with a scum collection bucket, a sedimentation sludge collection bucket and a sludge discharge pipe. The scum floating on the water surface enters the scum collection bucket through the slag hanger on the upper part of the scraper.
The sludge and sand particles deposited at the bottom of the pool are scraped into the sludge collection bucket by the scraper, and the sludge is discharged by regularly opening the sludge.
The valve is used to discharge the sludge, and the sludge is discharged
into the sludge collection tank.
1.3.6 Denitrification tank
After the primary sedimentation, the sewage contains high
nitrate nitrogen, and a certain amount of glucose is added to the tank, and the
nitrate in the sewage is converted into nitrogen by the denitrifying bacteria
in the tank, and the added organic matter is converted into carbon dioxide and
water at the same time. The designed HRT was 4 h.
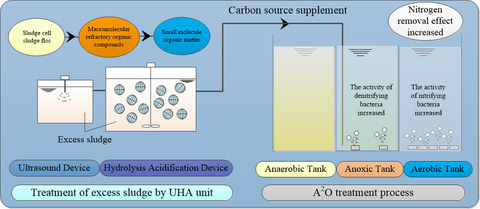
1.3.7 Hydrolysis and acidification pool
The macromolecular organic matter contained in the comprehensive sewage is difficult to be directly degraded by aerobic microorganisms.
In the hydrolytic acidification stage, the macromolecular
organic matter in the water is decomposed into easily biochemically small
molecular organic matter by the hydrolysis acidifying bacteria, thereby
improving the biodegradability of the wastewater. The effect of subsequent
biochemical treatment. The designed HRT was 8 h.
1.3.8 A2O
The phosphorus accumulating bacteria in the anaerobic tank absorb and degrade the organic matter quickly, and at the same time release the phosphorus in the body to prepare for the overabsorption of phosphorus under aerobic conditions. The designed HRT is 2 h.
The denitrifying bacteria in the anoxic tank use the The nitrate in the return water of the aerobic tank converts the organic matter from the effluent of the anaerobic tank into carbon dioxide and water, and at the same time, the nitrate in the return water of the aerobic tank is converted into nitrogen to realize biological denitrification and denitrification.
The designed HRT is 4 h. In the aerobic section, a membrane bioreactor (MBR) is used, and membrane filtration (microfiltration or ultrafiltration) is used to replace the sedimentation tank in the activated sludge process to achieve sludge-water separation. Under aerobic conditions of sewage, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria absorb excess phosphorus to achieve biological phosphorus removal, and at the same time complete the nitrification of ammonia nitrogen and the oxidation of organic matter.
Microorganisms and
other suspended solids are intercepted and separated by the membrane module,
the water is pumped to the intermediate pool by the suction pump through the
membrane module, and the excess sludge is discharged into the sludge collecting
pool. The designed HRT was 6 h.
1.4 Main equipment
The main structures and equipment are shown in Table 1 and
Table 2.
2 Debug and run
2.1 Chemical dephosphorization control of high phosphorus
wastewater
The high-phosphorus wastewater contains a lot of phosphate radicals. According to the nature of the wastewater, sodium hydroxide, calcium chloride, PAC and PAM are added to the coagulation and sedimentation tank of the phosphating wastewater in sequence, and the pH is controlled at 9.0 to 10.5.
The neutralization reaction tank is used to neutralize excess alkali, and
the pH is maintained at 7.5 to 8.0. The treated sewage is discharged into the
non-phosphating wastewater conditioning tank for subsequent treatment.
2.2 Activated sludge culture
Activated sludge cultivation adopts the method of inoculation and domestication. The inoculated sludge is taken from the dewatered sludge of the urban sewage treatment plant, and each unit is dosed according to 1% of its own volume. Then turn on the fan in turn to supply air to the denitrification, hydrolysis acidification and eutrophication units, turn on the anaerobic tank, and stir with a submersible mixer in the anoxic tank.
During the incubation period, the mass ratio of C, N, and P in the water should be kept at about 100:5:1. In the initial stage of commissioning, the organic load and hydraulic load are controlled at 1/4 of the design load, and the pH is controlled within the appropriate parameter range of each reaction unit.
In order to ensure that the nutrients and pH of the subsequent processing unit can be stabilized within the appropriate range.
Appropriate dextrose and sodium hydroxide can be added
to the treatment unit. After stable operation, 2.8 g of glucose was put into
the denitrification tank to provide sufficient carbon source for each ton of
sewage treated.
2.3 MBR debugging
When MBR is carried out, the biological treatment system is firstly cultivated with activated sludge. In the early stage of culturing, since the sludge has not been formed in large quantities and the sludge content is low, if the water is pumped from the membrane module by the suction pump, the pollution of the separation membrane in the aerobic tank will be aggravated, so the mass concentration of the sludge reaches 4 g.
Before /L, it is not suitable to start the suction pump to pump water from the membrane module, and choose the operation mode of intermittent water intake, gas stop, sedimentation and drainage from the temporary drainage pipe.
When the sludge
proliferates and reaches the required content, the number of suction pumps and
blowers to be turned on is determined according to the amount of influent
water. When the water output of the suction pump is turned on, it should be
controlled at about 1/3 of the designed water output, and should not be too
large; after 1 week of operation, it can be increased to about 2/3 of the
designed water output; after another 1 week of operation, adjust to the
designed water output.
2.4 Running effect
After 4 months of debugging, the effluent quality of each
structure is shown in Table 3.
It can be seen from Table 3 that the removal rates of COD, TN
and TP after treatment are 86.7%, 84.4% and 92%, respectively, and all effluent
indicators can reach the Grade A standard of GB 18918-2002.
Conclusion
For industrial parks, sewage of similar nature can be
centrally treated, which can not only reduce the cost of enterprise sewage
treatment, but also save resources.
Using denitrification-hydrolysis-acidification-anaerobic-anoxic-MBR
process to treat wastewater, the treatment effect is stable, and the effluent
is in the first-class A standard in GB 18918-2002. After further operation,
advanced treatment of sewage can be considered, and reverse osmosis technology
can be used to reuse sewage.

Comments
Post a Comment